Adaro Enterprise Risk Management
Each business entity within the three pillars of the Adaro Group (Adaro Energy, Adaro Minerals, and Adaro Green) is faced with various risks that must be managed in a structured, systematic, and consistent manner. Effective risk management requires the participation and support of all levels in the organization and can contribute to the both company sustainability and shareholder value creation. Internal and external risks, when not identified and managed effectively, can pose a threat to the Company’s going concern.
Adaro Risk Management Policy
To strengthen Adaro's Risk Management Governance, the Company has a Risk Management Policy as a form of the Company's commitment to integrated risk management.
Below are the Commitments of Adaro's Risk Management Policy:

Adaro Risk Management Standard
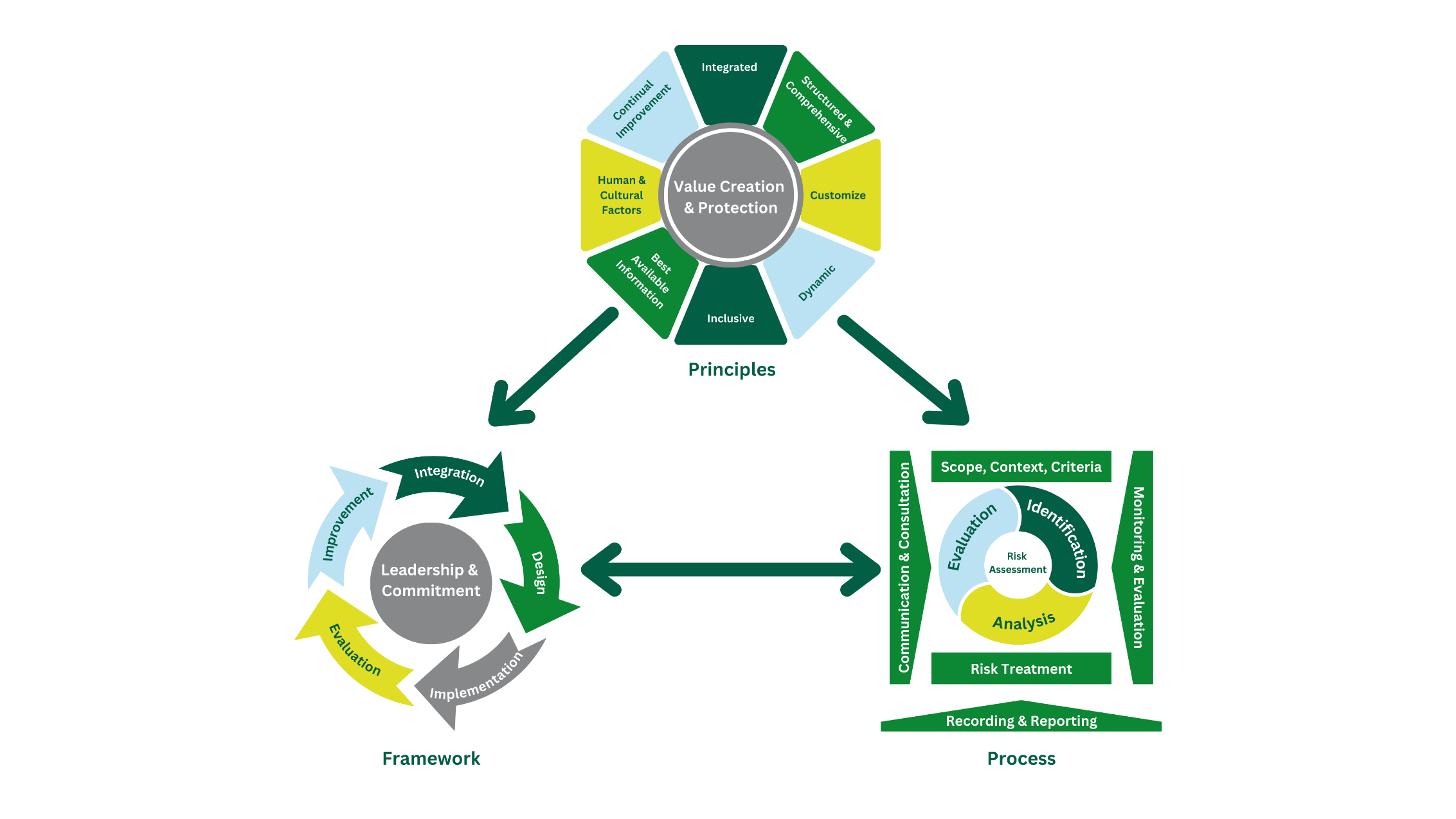
Adaro Risk Management Standard
To strengthen the implementation of Adaro's risk management policy, the Company has developed risk management standards tailored to its needs by adopting ISO 31000:2018 – Risk Management Guidelines.
Adaro's risk management standards consist of three main components:
- Risk management principle
- Integrated
- Structured & comprehensive
- Customized
- Inclusive
- Dynamic
- Best available information
- Human and culture factors
- Continuous improvement
- Risk management framework, consisting of:
- Leadership and commitment:
- Issuing risk management statement or policy.
- Ensuring resource availability.
- Determining authority, responsibility, and accountability.
- Adjusting and implementing all components of the framework.
- Integration of risk management into the entire business processes, through:
- Planning, implementation, and achievement of company targets and goals.
- Business process and project management.
- HSE management.
- Crisis management.
- Internal audit.
- Design
With the philosophy “make it clear, make it simple”, risk management is designed to consist of three levels: strategic, tactical, and operational.
- Implementation
Risk management is implemented by top down and bottom-up approaches to ensure the integration of the parent company and subsidiaries’ risk management using ORMP approach (objective, risk, mitigation and planning).
- Evaluation
The management determines the risk management targets, regularly measures the progress through maturity level assessment and risk culture survey, reviews the policy and technical guideline, and monitors the effectiveness of risk management framework and process.
- Risk management improvement
The evaluation outcome is followed up to improve risk management continuously.
- Leadership and commitment:
- Risk management process
- Communication and consultation.
- Determination of scope, context, and criteria.
- Risk identification, analysis, and evaluation.
- Risk treatment.
- Risk monitoring and review.
- Recording and reporting.
Adaro Risk Management Three Lines Model
The three lines model is used to ensure checks and balances:
- First line: Board of Directors and director in-charge, who are responsible for identifying and managing risks.
- Second line: all corporate functions excluding Internal Audit Division, responsible for providing risk expertise, support, monitoring, and evaluation, including determining the policy, standard, technical guideline, and other risk management tools.
- Third line: Internal Audit Division, responsible for providing independent and objective assurance on control (governance, risk management, and internal control). Additional assurance from external parties is also possible, such as from external auditor.
Adaro Risk Profile
Adaro has identified 29 types of risks, covering external, operational, and organizational aspects, integrated across all its business lines. These 29 types of risks are:
|
Risk Type |
|
|
External Environment |
Macroeconomic |
|
Industry |
|
|
Regulation Changes |
|
|
Community Relation |
|
|
Security Threat |
|
|
Weather |
|
|
Natural Disaster |
|
|
Investment |
|
|
Operational |
HSE |
|
Critical Materials |
|
|
Production Disruption |
|
|
Product Quality |
|
|
Facility & Infrastructure |
|
|
Contractor |
|
|
Capacity |
|
|
Operation Planning |
|
|
Business Interruption |
|
|
Land Availability |
|
|
Project |
|
|
Sales Effectiveness |
|
|
Coal Reserve |
|
|
Production Cost |
|
|
Organizational |
People |
|
Governance |
|
|
Business Process |
|
|
Financial |
|
|
Technology |
|
|
Legal & Regulatory Compliance |
|
|
Financial Reporting |
|
As of December 2023, Adaro has identified 10 focus risks: HSE, project, industry, community relations, macroeconomic, legal and regulatory compliance, regulation changes, weather, business disruption, and land availability.
For more detailed information about our risk management, please refer to the 2023 Annual Report on page 288.
Adaro Crisis Management
Adaro has implemented a Crisis Management Policy since 2015 to ensure that each subsidiary is prepared to continue operating during a crisis. This policy aims to ensure the operational resilience of Adaro and its subsidiaries in facing risks with catastrophic impacts.
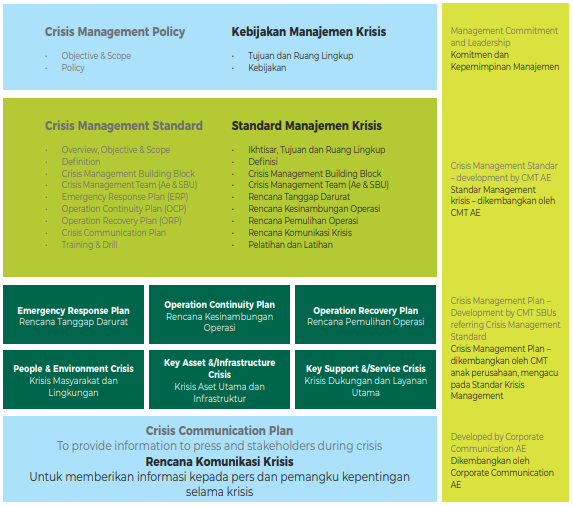
Adaro Crisis Management Building Block
Adaro has developed a crisis management building block, consisting of:
- Crisis Management Policy
- Crisis Management Standard
This standard serves as a reference for the crisis management plan developed by the subsidiaries to be the response on crisis events, which consists of three main components:
- Emergency Response Plan (ERP): the initial response to the incidents leading to crisis, with the main objectives to ensure the safety of the employees, visitors, and surrounding communities, to minimize environmental damage or contamination, and to protect operations from further damage or disturbance throughout or after the incidents.
- Operational Continuity Plan (OCP): containing a set of actions for continuing operations as soon as possible with the limited resources and/or infrastructure available after the incidents, as well as the contact numbers of the relevant authority, vendors, and functions.
- Operational Recovery Plan (ORP): containing a set of actions for returning operations to the conditions before the crisis with information of the duration needed for recovery, and information on the contact numbers of the relevant authority, vendors, and functions.
- Crisis Communication Plan
The Corporate Communications Division has developed the Crisis Communication Plan to be used as a guideline for sharing information with the media and stakeholders during a crisis.
Review on the effectiveness of risk management system
Survey on risk culture
To maintain effective risk management, Adaro periodically conducts a Risk Culture Survey with the involvement of an independent third party. This ensures objective instruments, methodology, and results. The survey results are then reviewed and presented to the Risk Owner for continuous improvement.
